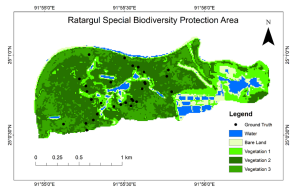
Forest degradation is threatening the biodiversity of moist tropical forests since the beginning of their development. Bangladesh is losing its forests and associated biodiversity continuously due to forest-dependent livelihoods. The only freshwater swamp forest of the Ratargul Special Biodiversity Protection Area in Bangladesh is also very prone to degradation due to anthropogenic disturbance. This distinct swamp forest has unique biological diversity compared to other forest types. To assess its degradation and to propose implications for conservation, sentinel images with 10×10 m resolution were used. Also, field data were collected and analyzed. This research produced a map of forest cover change and outlined an area that can be used in restoration planning. Branch cutting, dry season overgrazing, illegal tree felling, fuelwood collection, trampling by tourists, and insect and disease epidemics were identified as causes of degradation. Functional conservation effort ensured by strong political will and area-specific forest protection regulation is essential for the conservation of last swamp forest and its remnant biodiversity. Community-based conservation approaches need to be applied for mass awareness regarding this ecosystem's value and its sustainability.
Ratargul Özel Biyoçeşitlilik Koruma Alanındaki koruma önerileri kapsamında ormandaki bozulmanın değerlendirilmesi
Ormanların bozulması, var oldukları günden bugüne nemli tropik ormanların biyolojik çeşitliliğini tehdit etmektedir. Bangladeş, ormana dayalı geçim kaynakları nedeniyle ormanlarını ve ilişkili biyolojik çeşitliliğini sürekli olarak kaybetmektedir. Bangladeş'teki Ratargul Özel Biyoçeşitlilik Koruma Bölgesi'nin tek su basar ormanı da antropojenik etkilerden dolayı bozulmaya çok eğilimlidir. Bu farklı su basar ormanı, diğer orman türlerine kıyasla benzersiz biyolojik çeşitliliğe sahiptir. Bu alandaki bozunmanın değerlendirilmesi ve korumaya yönelik önerilerde bulunabilmek için 10 × 10 m çözünürlüklü sentinel görüntüleri kullanılmış olup, ayrıca alandan toplanan veriler de analiz edilmiştir. Bu araştırma, orman örtüsü değişiminin bir haritasını çıkarmış ve restorasyon planlamasında kullanılabilecek bir alanı ortaya koymuştur. Ağaç dallarının kesilmesi, kurak mevsimde aşırı otlatmaların yapılması, yasadışı ağaç kesimi, yakacak odun toplama, turistlerin dolaşması ile toprağın sıkıştırılması, böcek ve hastalık salgınları ormandaki bozulmanın nedenleri olarak belirlenmiştir. Güçlü siyasi irade ve bölgeye özgü orman koruma düzenlemesi ile sağlanan işlevsel koruma çabası, son su basar ormanının ve kalan biyolojik çeşitliliğinin korunması için gerekli görülmektedir. Bu ekosistemin değeri ve sürdürülebilirliği konusunda kitlesel farkındalık için topluluk temelli koruma yaklaşımlarının uygulanması gerekmektedir.
Cite this paper as: Humayun-Bin-Akram, M., Masum, K.M., 2020. Forest degradation assessment of Ratargul Special Biodiversity Protection Area for conservation implications. Forestist 70(2): 77-84.




.png)